Prevalence estimated at 1/800,000. Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the CPS1 gene (2q35) coding for carbamyl phosphate synthetase I, the mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate, the first step in the urea cycle. Its absence results in a severe and rare disorder of urea cycle metabolism, characterized by
- severe hyperammonemia of neonatal onset, occurring several days after birth and manifesting as lethargy, delayed growth, vomiting, hypothermia, convulsions, coma and death,
- or late in childhood or adulthood, with more moderate symptoms of hyperammonemia.
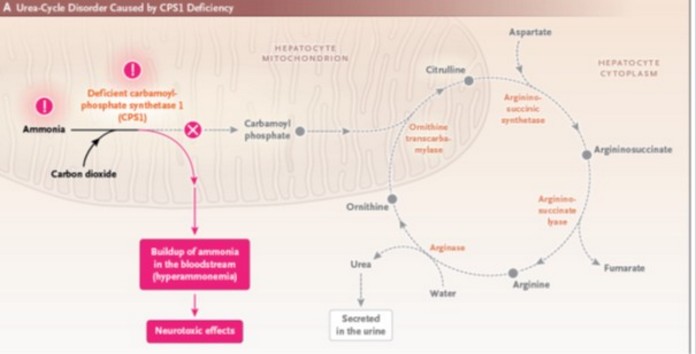
Source: NEJM
Carbamyl phosphate synthetase II (CAD gene (2p23.3)) is an ubiquitous cytoplasmic protein involved in the metabolism of pyrimidines.
Anesthetic implications:
see urea cycle. Shorten the duration of preoperative fasting: administer a glucose-containing solution as soon as the fasting period begins. Empty the stomach to avoid any hidden protein intake through the digestive tract in case of surgery where blood can be swallowed (ENT, stomatology). Special monitoring: NH4 (nl < 50 µmol/L), blood glucose. Use an anesthesia strategy that reduces the stress response: locoregional anesthesia, opioids, optimal postoperative analgesia.
References :
- Dobbelaere D, Mention K.
Déficits du cycle de l’urée in Maladies métaboliques héréditaires, éditeurs B Chabrol et P de Lonlay,
Progrès en pédiatrie n°29, p139-147, Doin 2011
- Del Rio C, Martin-Hernandez E, Ruiz A, Quijada-Fraille P, Rubio P.
Perioperative management of children with urea cycle disorders.
Pediatr Anesth 2020; 30:780-91.
- Matsushita H, Fujiyoshi T, Yoshimaru K, Matsuura , Mushimoto Y, Karashima Y, Yamaura K.
Anesthesia management in living‑donor liver transplantation in a patient with carbamoyl phosphate synthetase deficiency: a case report.
JA Clinical Reports 2022 ; 8:71 doi.org/10.1186/s40981-022-00558-9
- Musunuru K, Grandinette SA, Wang X, Hudson TR,3 Briseno K, Berry AM, Hacker JL et al.
Patient-specific in vivo gene editing to treat a rare genetic disease.
NEJM, May 2025. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2504747
Updated: May 2025