Very rare: < 1/106. It is most severe form of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency (see this term) that results in cholesterol esters overload. Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the LIPA or LAL genes on 10q24-q25. This deficiency leads to a massive accumulation in tissues of esterified cholesterol and triglycerides of lipoproteic origin.
Onset in the first weeks of life:
- abdominal distention with important hepatosplenomegaly, sometimes ascites; vomiting
- diarrhea by steatorrhea
- calcification of the adrenal glands by accumulation of cholesterol crystals and necrosis (characteristic sign)
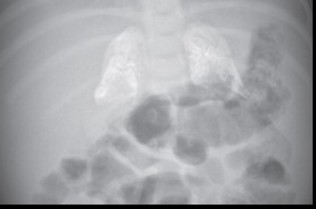
- anemia without thrombocytopenia, cachexia
- death before 12 months of age without treatment: very early bone marrow or stem cells transplantation can be life-saving. Experimental treatment: sebelipase alpha IV once a week.
Replacement therapy: sebelipase alpha IV 1X/week
Recent success with complete cure in an infant: replacement therapy (sebelipase) quickly combined with rituximab (to avoid the appearance of anti-sebelipase antibodies) and followed by stem cells (cord blood) transplant.
Diagnosis: vacuolated lymphocytes, foamy histiocytes in the bone marrow, very low activity of acidic lipase (< 6%) in leukocytes.
Anesthetic implications:
anemia, hepatosplenomegaly with portal hypertension; no adrenal insufficiency reported despite the adrenal calcifications. Avoid a propofol-based TIVA (triglycerides overload)
References :
- Al Essa M, Nounou R, Sakati N, Le Quesne G et al.
Wolman’s disease: the King Faisal specialist hospital and research centre experience.
Annals of Saudi Medicine 1998; 18: 120-4.
- Rodriguez-Oquendo A, Kwiterovich PO.
Dyslipidaemias. In Inborn Metabolic Diseases, 5th ed, Editors : Saudubray J-M, van den Berghe G, Walter JH. Springer 2012, p 439-60.
- Ben Hassine L, Lahmar L, Louati H, Douira W, Bellagha I.
Maladie de Wolman.
Arch Pédiatr 2016 ; 23 : 1201-3.
- Krause I, Gavrielli H.
Adrenal calcifications in an infant.
NEJM 2018; 378: e36
- Eskandari SK, Revenich EGM, Pot DJ, de Boer F, Bierings M, van Spronsen FJ, van Hasselt PM, Lindemans CA, Lubout CMA.
High-dose ERT, Rituximab, and early HSCT in an infant with Wolman’s disease.
N Engl J Med 2024;390:623-9.
Updated: March 2024