(Hepato-lenticular degeneration)
Prevalence: 1/30,000 to 1/100.000. Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the ATP7B gene on 13q14.3. Accumulation of copper in the liver and brain following a dysfunction of a ATPase-type protein involved in the transport of intra- and extracellular Cu. Plasma ceruloplasmin level is less than 30% of normal values.
Clinical presentation:
- either hepatic (30 %): rare symptoms before the age of 5 years; first symptoms usually between 10 and 14 years of age; clinical picture of chronic hepatitis; progressive cirrhosis with hepatosplenomegaly; presents sometimes fulminant hepatitis
- or neurological (40-50 %) associated with cirrhosis: symptoms around the age of 7-8 years: reduction of facial mimicry, dysphagia, dysarthria, intentional tremor, dyskinesia
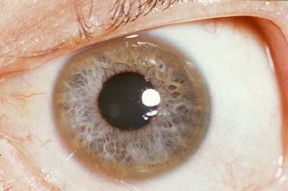
Presence of a corneal Kayser-Fleischer ring: brownish-yellow-green ring around the corneoscleral junction.
Sopmetimes: proteinuria, cystolithiasis
MRI: 'double-panda sign' - face of the giant panda sign at the level of the mid brain and face of the miniature panda sign at the level of the pons.
Treatment: d-penicillamine (regression of neurological signs), zinc or trientine (triethylenetetramine).
Anesthetic implications:
cirrhosis. Liver failure.
References :
- Sharawat IK, Kurup A, Sondhi V, Saini L.
Boy with dysarthria and frequent falls: a treatable disorder.
J Pediatr 2019; 215: 280-1
Updated: December 2019