Prevalence: 3 to 10 /10,000 births. Malformation of fingers and/or toes that are totally or partly fused (due, for example, to a disorder of physiological apoptosis of the interdigital skin) during the formation of the extremities. The toes are more frequently affected than fingers, and boys twice more often than girls. There are so-called syndromic forms (associated with a syndrome such as Apert syndrome, for example) or isolated. Several classifications have been described.
The simplest is one that describes the following forms:
- preaxial: when the radial ray (or the side of the big toe) is affected
- mesoaxial: when the middle part of the extremity is involved
- postaxial: when the ulnar ray (or the side of the little toe) is involved
- and total
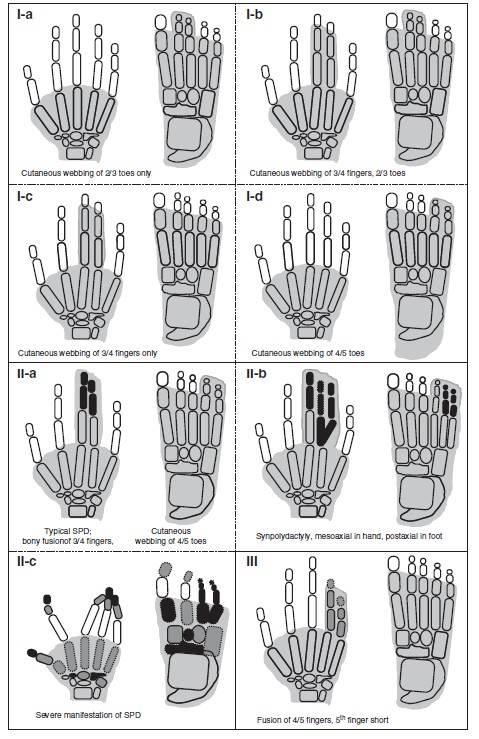
A fuller and more complex of isolated syndactylies classification is that of Temtamy-McKusick recently extended and adapted to the new data of molecular genetics (see figures).
|
|
type |
MIM |
fingers |
toes |
transmission |
locus |
|
I has |
ZD1 zygodactyly |
609 815 |
NL |
2 and 3 |
AD |
3p21.31 |
|
I b |
SD1 Lueken |
185 900 |
3 and 4, skin |
2 and 3, skin |
AD |
2q34-q36 |
|
I c |
Montagu |
|
3 and 4, skin and bone |
NL |
AD |
|
|
I d |
Castilla |
|
NL |
4 and 5, skin |
AD ? |
|
|
II |
SPD1 Vordingborg |
186 000 |
mesoaxial SPD (3 and 4) |
Postaxial SPD (4 and 5) |
AD |
2q31 (HOXD13) |
|
IIb |
SPD2 Debeer |
608 180 |
SPD central and postaxial |
postaxial |
AD |
22q13.3 (FBLN1) |
|
IIc |
SPD3 Malik |
610 234 |
central SPD |
postaxial SPD |
AD |
14q11.2-q13 |
|
III |
SDTY3; ODDD; Johnson-Kirby |
186 100 |
4-5, 5th short finger |
NL |
AD |
6q21-q23 (GJA1) |
|
IV |
SDTY4 Haas |
186 200 |
all fingers, polydactyly pre and postaxial |
NL |
AD |
7q36 (LMBR1) |
|
IV b |
Andersen-Hansen |
|
webbing and all fingers, pre polydactyly postaxial |
variable webbing and polydactyly |
AD |
|
|
V |
SDTY5; Dowd |
186 300 |
4/5 with fusion hypoplastic metacarpals |
mesoaxial |
AD |
2q31 (HOWD13) |
|
VI |
Mitten |
|
2/5 |
2/5 |
AD |
|
|
VII |
Cenani-Lenz hands in spoon |
212 780 |
bone syndactyly complete with fusion of the metacarpals |
bone syndactyly complete with fusion of the metatarsals |
AR |
11p12-p11.2 (LRP4) |
|
VII b |
oligodactyly |
|
little distortion |
variable syndactyly |
AD |
15q13.3 (GREM1-FMN1) |
|
VIIIa |
Orel-Holmes |
309 630 |
4/5 fusion metacarpals |
NL |
XR |
|
|
VIIIb |
LERCH |
|
4/5 fusion metacarpals |
NL |
AD |
|
|
IX |
MSSD Malik-Daudi |
609 432 |
mesoaxial synostosis with phalangeal reduction |
preaxial webbing with phalangeal hypoplasia |
AR |
17p13.3 |
SPD = synpolydactyly = association of syndactyly and a polydactyly
AD = autosomal dominant, AR = autosomale recessive, X = X-linked
NL = normal SPD = SynPolyDactyly

Anesthetic implications:
check for associated anomalies, anticipate difficult peripheral venous access .
References :
- Malik S.
Syndactyly : phenotypes, genetics and current classification.
Eur J Human Genet 2012 ; 20 : 817-24
Updated: June 2015