(SOPH syndrome)
Extremely rare, especially described in the Yakut population (native Californians and inhabitants of North Siberia). Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the NBAS gene (neuroblastoma amplified sequence) (2p24.3) . The NBAS gene is coexpressed in excess with the MYC gene in neuroblastoma. The protein coded by NBAS is a component of the synthaxin 18 complex. Synthaxin 18 is a key element of the retrograde vesicular transport from the Golgi bodies to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Association of:
- short stature due to a postnatal growth delay
- bilateral optic nerve atrophy with achromatopsia and loss of visual acuity
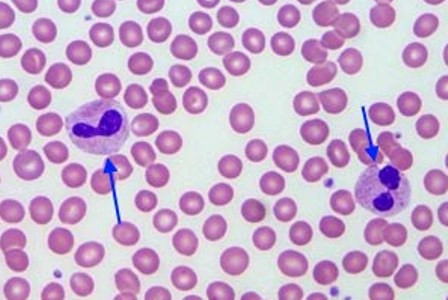
- Pelger-Huet anomaly in the blood smear: unusual lobulation of the nuclei of neutrophil and eosinophilic granulocytes (bilobed, peanut or dumbbell-shaped) and unusual structure (coarse and lumpy)
- facial dysmorphism: brachycephaly with elongated face and narrow forehead, small orbits with relative exophthalmia, malar hypoplasia, elongated philtrum, senile-appearing skin, thin hair, bushy eyebrows
- wide spread big toes
Some mutations cause recurrent episodes of acute liver failure, after febrile episodes without any of the other signs of the syndrome (see Acute infantile liver failure associated to fever [MIM 616 483] . The liver function returns to normal between those episodes that disappear generally after 4 years of age.
Anesthetic implications:
unknown; check the liver function
References :
- Cardenas V, DiPaola F, Adams SD, Holtz AM, Ahmad A.
Acute liver failure secondary to neuroblastoma amplified sequence deficiency.
J Pediatr 2017; 186: 179-82. - Kortum F, Marquardt I, Alawi M, Korenke GC et al.
Acute liver failure meets SOPH syndrome :a case report on an intermediate phenotype.
Pediatrics 2017 ; 139: e20160550 - Chavany J, Cano A, Roquelaure B, Bourgeois P et al.
Mutations in NBAS ans SCYL1, genetic causes of recurrent liver failure in children : three case reports and literature review.
Arch Pediatr 2020 ; 27 : 155-9
Updated: July 2020