(Mucopolysaccharidosis type III)
Prevalence: 1/58,000. Autosomal recessive transmission. Mucopolysaccharidosis type III due to a lysosomal disease causing the accumulation of heparan sulfate in the organs and tissues of the body.
Four subtypes are distinguished according to the defective lysosomal enzyme:
- A: heparan-N-sulfatase gene on 17q25.3 [MIM 252 900] ; experimental treatment with fluoxetine
- B: N-acetyl-α-glucosaminidase gene on 17q21.2 [MIM 252 920]
- C: α-glucosaminide N-acetyltransferase gene on 8p11.2-p11.1 [MIM 252 930]
- D: N- acetylglucosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase gene on 12q14.3 [MIM 252 940]
These subtypes are clinically distinguishable. The A form is the most common and most severe.
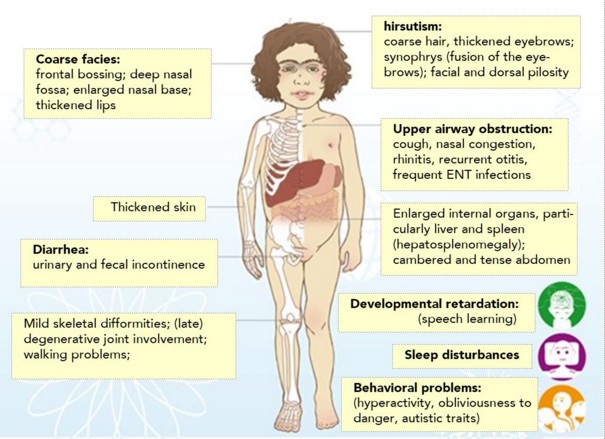
Development is normal until about 2-3 years of age. Between the age of 2 and 5 years, there is a regression of mental functions, behaviour disorders (aggression, tantrums) , seizures, progressive deafness, progressive motor disorders leading to the loss of the walking around the age of 10 years. Facies changes are retarded. Hirsutism. Discrete hepatomegaly. No cardiac or pulmonary problem, except at the end of life (inhalation pneumonia). However, in a cohort of 34 patients, 13 presented with an anatomical (moderate mitral or aortic involvement) or functional (LVH, LV diastolic dysfunction) anomaly of the heart while some others presented with hemostasis disorders.
Anesthetic implications:
mask ventilation and intubation are not particularly difficult, contrary to other mucopolysaccharidoses.
References:
- Cingi EC, Beebe DS, Whitley CB, Belni KG.
Anesthetic care and perioperative complications in children with Sanfilippo syndrome type A.
Pediatr Anesth 2016; 26:531-538
- Cohen MA, Stuart GM.
Delivery of anesthesia for children with mucopolysaccharidosis type III (Sanfilippo syndrome): a review of 86 anesthetics.
Pediatr Anesth 2017; 27: 363-9.
- Kamata M, McKee C, Truxal KV, Flanigan KM et al.
General anesthesia with a native airway for patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type III.
Pediatr Anesth 2017; 27: 370-376
Updated: May 2022