[MIM 180 849, 610 543, 613 684]
Prevalence: 1/125,000. Usually de novo mutation, rarely autosomal dominant transmission of a mutation of the CBP gene on 16p13.3 (70 %) or EP300 gene on 22q13 (type 2, less severe phenotype). Dysmorphic syndrome associating severe mental retardation (I.Q. 40-50 wich speech disorders), growth retardation (microcephaly in 46%), a characteristic aspect of the extremities (wide thumbs and big toes, sometimes with axial angulation) and of the face:
- in utero: sometimes, polyhydramnios, in utero growth deficit
- newborn: high forehead, upslanting palpebral fissures, micrognathia, pseudohypertelorism, ptosis, high-arched palate (sometimes cleft-palate), low-set ears
- later: downslanting palpebral fissures, long and protruding nasal septum, beaked nose; high-arched eyebrows; maxillary hypoplasia
- typically: eye closure when smiling
- adult: behavioural disorders, overweight.
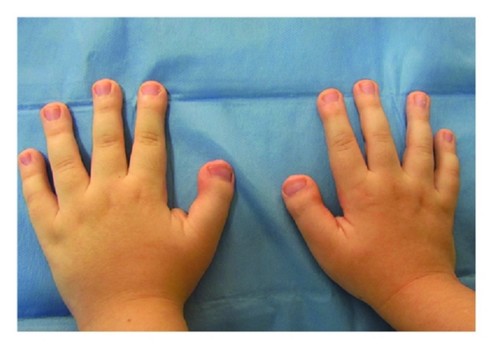
Frequently associated:
- kidney abnormalities (50 %): hydronephrosis, urinary tract duplication, vesicoureteral reflux
- congenital heart disease (30 %): ASD, VSD, ductus arteriosus, aortic coarctation, pulmonary stenosis, bicuspid aortic valve,
- gastroesophageal reflux,
- eye anomalies: hypertelorism, epicanthus, long eyelashes, nasolacrymal duct obstruction, strabismus, ptosis,uni- or bilateral corneal anomalies, coloboma, glaucoma, congenital cataract, retinal dystrophy or optic nerve hypoplasia.
- moderate deafness (23 %)
- epilepsy (convulsions in 28 % of cases but abnormal EEG in 57-66 % of cases)
- tendency to cheloid scares
- tendency to constipation.
Some cases of:
- anomalies of the cervical vertebrae with risk of cervical myelopathy: C1-C2 instability, hypoplastic odontoid, os osteoideum (see this term), fusion of vertebrae, hemivertebrae
- tracheomalacia
- spina bifida occulta or signs of spinal compression (cervical or at the level of the conus terminalis)
- agenesis of the corpus callosum
There is an increased risk of leukemia, brain tumors (medulloblastoma, meningioma) but also neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma and pilomatrixomas.
Anesthetic implications:
risk of difficult intubation (micrognathia, narrow larynx ?). Risk of inhalation or regurgitation. Preoperative evaluation of the cervical spine and the renal function. Echocardiography. Obstructive sleep apneas. Isolated cases of arrhythmia after the use of succinylcholine. Risk of delayed emergence from anesthesia.
References :
- Robson MJ, Brown LM, Sharrard WJW.
Cervical spondylolithesis and other skeletal abnormalities in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
J Bone & Joint Surg 1980; 62B: 297-300 - van Genderen MM, Kinds GF, Riemslag FCC, Hennekam RCM.
Ocular features in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: investigation of 24 patients and review of the literature.
Br J Ophthalmol 2000; 84:1177-84 - Critchley LA, Gin T, Stuart JC.
Anaesthesia in an infant with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
Anaesthesia 1995; 50:37-8. - Stirt JA.
Anesthetic problems in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
Anesth Analg 1981 ; 60 : 534-6. - Dunckley CJA, Dearlove OR.
Delayed recovery from anaesthesia in Rubisntein-Taybi syndrome.
Paediatr Anaesth 1996; 6: 245-6. - Khanna P, Baidya DK, Vinayr T, Agarwal A.
Successful use of air-Q intubating laryngeal airway after failed rapid sequence intubation in a child with Rubnstein-Taybi syndrome.
Indian J Anaesth 2013; 57: 203-4. - Dearlove OR, Perkins R.
Anaesthesia in an adult with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
Br J Anaesth 2003; 90: 399-400 - Yamamoto T, Kurosawa K, Masuno M, Okuzumi S et al.
Congenital anomaly of cervical vertebrae is a major complication of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome.
Am J Med Genet 2005; 135A: 130-3 - Agarwal S, Ahmad YH, Talpesh M, Zestos M.
Anesthetic management of children with Rubinstein –Taybi syndrome.
MEJ Anesth 2011; 21: 309-13. - Dharmalingam TK, Liew Sat Lin C, Muniandy RK.
Prolonged paralysis with atracurium use in a patient with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.
BMJ Case Rep. 2018;10.1136/bcr-2017-222692 - Moheb N, Khosa S, Trikaji B, Mishra SK.
Neurological manifestations of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: a case report.
SM Genetic Synd Gene Ther 2018; 2: 1003-4 - Frost EAM.
Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.
Anesthesiologynews.com 54581, April 16, 2019. 6p
Updated: January 2020