Benign, sometimes self-limiting disorder of children and adolescents. It is a non-Langerhans histiocytosis associated with massive cervical lymphadenopathies, the origin of which is either infectious (unknown agent) or autoimmune (forms with systemic manifestations). Symptoms: massive cervical lymphadenopathies, fever, inflammatory syndrome.
Other possible locations : skin, eye (exophthalmia), upper airway (larynx or trachea tumor), salivary glands, central nervous system (mass effect), thyroid (nodules), bone (lytic lesions), ovaries, breasts.
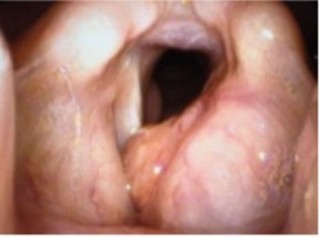
Yellowish mucous mass in the left laryngeal ventricule
In case of autoimmune process: steroids, immunosuppression (sirolimus)
Anesthetic implications:
in case of involvement of the upper airway: obstruction of the respiratory tract, obstructive sleep apnea, superior vena cava syndrome; risk of difficult intubation; immunosuppression.
References :
- Khanna P, Garg R, Sunder RA.
Rosai-Dorfman disease: perianesthetic concerns.
Acta Anaesth Belg 2010; 61: 1-3.
- Fuentes-Garcia D, Hernandez-Palazon J, Carceles-Baron MD, Acosta-Villegas F.
Anaesthesia for a paediatric patient with Rosai-Dorfman disease.
Br J Anaesth 2010; 105: 389. - Sridhara SK, Reyes C, Shah RK.
Rosai-Dorfman disease in the submandibular salivary glands of a pediatric patient.
Int J Pediar Otorhinolaryngol Extra 2012; 7: 200-2. - Sivakoti K, Niazi M, Kronfeld G et al.
Sinus histiocytosis and massive lymphadenothy (Rosai-Dorfman disease) mimicking cervical lymphadenitis.
J Pediatr 2014; 164: 943-4. - Moore SM, Astle J, Shay SG.
Cervical lymphadenopathy and airway masses in a child.
JAMAOtoLaryngology doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2022.3576 - Ramos-Gonzalez G, Soltani T, Nnamdi-Nwosu O, Fagen K, Chamizo W, Chandler N.
Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the breast in a 13-year-old female: a case report.
J Pediatr Surgery Case Reports 2023 ; 96 : 102690, doi.org/10.1016/j.epsc.2023.102690
Updated: May 2024