(pseudothalidomide, SC-phocomelia syndrome)
Very rare. Autosomal recessive mutation of the ESCO2 gene (8p21.2).
Diagnosis by examination of the chromosomes in metaphase: premature separation of centromeric heterochromatin.
Great variability of presentation with the combination of :
- intrauterine growth restriction:
- malformation of the limbs (more severe in upper limbs): tetraphocomelia or quasi-symmetrical amelia; malformations of the hands or feet, the upper limb is generally more affected; flexion contractures
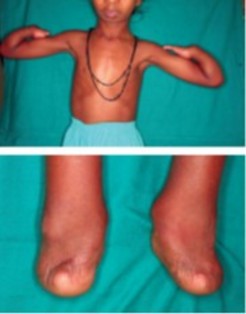
- craniofacial abnormalities: cleft lip with or without cleft palate, micrognathia, microbrachycephaly, hypertelorism, downwards slanting palpebral fissures, shallow orbits with prominent eyes.
Frequent mental retardation. Sometimes: pulmonary hypoplasia, cardiac abnormalities (ASD, ductus arteriosus) , renal polycystic disease, urogenital malformations, Moyamoya disease.
Often letal in the neonatal period or early infancy.
Anesthetic implications:
hypoxemia, difficult venous access, difficult intubation; also difficult monitoring (saturation, BP). A case of reliable measurement using a neonatal cuff placed around the penis has been reported.
References :
- Ragavan M, Reddy S, Kumar S.
Tetra-amelia with lung hypoplasia and facial defects, Robers-SC syndrome : report of two cases.
Pediatr Surg Int 2010; 26: 1049-52.
- Tallmeister A, Sheehan MM, Pelton DA.
Dental anaesthesia for a child with complete amelia.
Can Anaesth Soc J 1986; 33: 484-7. - Gurnaney H, Ganesh A, Storm PB.
Penile blood pressure monitoring in a pediatric patient with hypomelia.
Anesth Analg 2010; 111; 1328. - Murthy J, Dewan M, Hussain A.
Roberts-SC syndrome, a rare syndrome and cleft palate repair.
Indian J Plast Surg 2008 ; 41:222-5
Updated: May 2025