(Mosaic Pallister syndrome, Pallister-Killian-Teschler-Nicola syndrome, Teschler-Nicola-Killian syndrome, mosaicism of isochromosome 12)
Prevalence: 1/25.000. Tetrasomy of the short arm of chromosome 12 (12 p).
Association of:
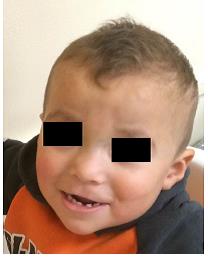
- facial dysmorphism: coarse features with a flat occiput (plagiocephaly), a high forehead, poorly marked supraorbital edges, downslanting palpebral fissures, hypertelorism, a flat and broad nasal root, a short nose with anteverted nostrils, large mouth with low-set commissures and prominent upper lip; a long philtrum or invasion insertion vermilion line of the upper lip with skin of the philtrum ('Pallister lip') (see picture). With age, macroglossia and a pointed chin appear.
- rhizomelic shortening of the limbs, short hands and feet with ungual hypoplasia.
- anomalies of skin pigmentation: streaks or spots of hypo or hyperpigmentation
- short neck
- bifid uvula
- frontotmporal balding with sparse eyebrows and eyelashes
- deep mental retardation with epilepsy.
Frequent congenital diaphragmatic hernia (50 %). Cardiovascular problems (ASD,VSD). Hypotonia is present at birth and contractures develop with age.
Anesthetic implications:
refractory epilepsy, profound mental disability, risk of difficult intubation.
References :
- Knab J, Heupel EW, Steinmann D.
Anesthesia for orthopedic surgery in Pallister-Killian syndrome.
Pediatr Anesth 2008; 18: 682-4.
- Kira S.
Anesthetic management of Pallister-Killian syndrome using a Bispectral index monitor in a patient with severe seizures.
J Clin Anesth 2011; 23: 674-6.
- Stone L, Tripuraveni R, Bain M, Hernandez C.
Pallister-Killian syndrome in a two years-old boy.
Clin Case Reports 2017; 774-7
Updated: October 2018