Rare. Two types have been identified:
- type 1 [MIM 166 780] or Fara-Chlupackova syndrome: autosomal dominant transmission of a more or less severe deletion on 8q13.3 where the EYA1 gene is located (adjacent genes)
- type 2 [MIM 167 411]: autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the PAX1 gene (20p11.22)
Association of:
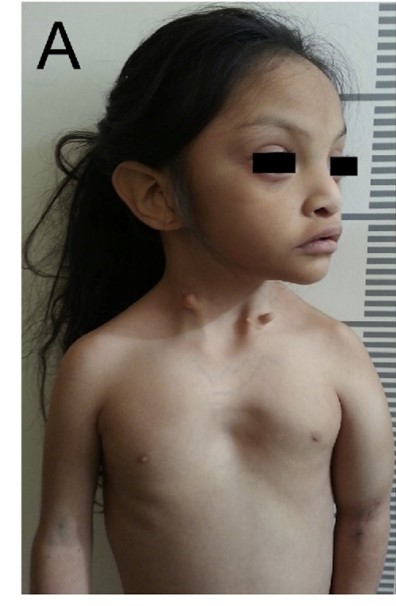
- auricular anomalies: cupped low-set ears with hypoplasia of the lobes, tragus and antitragus; preauricular fistulas and/or cysts, anomalies of the branchial arches, hypoacousia or deafness
- facial dysmorphism: triangular face with a wide forehead and narrow nose and mandibulae
- skeletal anomalies: vertebral anomalies, elongated neck with hypoplastic cervical muscles, low-set clavicles, low-set winged scapulae, sloping shoulders, pectus excavatum.
- mild intellectual disability
- frequent short stature
- in case of type 2, 'T' type immunodeficiency linked to thymic dysfunction, causing repeated infections
Anesthetic implications:
echoguided central venous access, antibioprophylaxis, check the absence of local vertebral anomalies before any neuraxial block; risk of difficult intubation due to the branchial arches anomalies
References :
-
Updated: October 2022