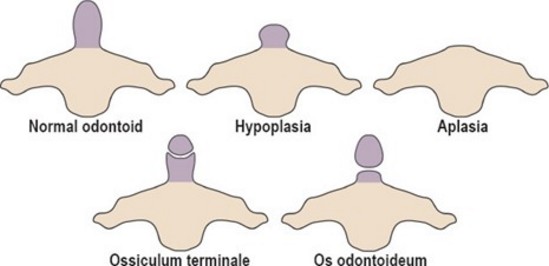
Congenital anomaly of the formation of the axis: the dens of axis is not fused to its body.
This is the result of :
- either the absence of fusion of the ossification nucleus of the odontoid process with that of the axis body,
- or an acquired form resulting from an undisplaced, unrecognized fracture of the growth plate (before 5-6 years of age).
As a result the atlo-axis joint is unstable.
A distinction is made between :
- orthotopic form: the dens axis is in its normal anatomical position
- dystopic form: the anatomical position is abnormal
This malformation can be isolated or associated with other anomalies:
- trisomy 21 , Klippel-Feil syndrome, Morquio syndrome, some multiple epiphyseal dysplasia
- occipitalisation of C1 or basilar impression.
Symptomatology: none or cervicalgia, torticollis, vertigo, acute quadriparesis.
Hyperextension of the neck can cause a significant decrease in the diameter of the spinal canal with cervical cord compression. One can divide the surface of the medullary canal at the C1 level in three identical areas (Steel’s rule): 1/3 for the odontoid process, 1/3 for the spinal cord and 1/3 of free space. This free space is the margin of safety that prevents spinal compression during extreme movements of the cervical spine, specially at the level of the occipito-atloido-axial joint.
Differential diagnosis:
- odontoid fracture type 2
- persistence of the terminal ossiculum
Anesthetic implications:
avoid movements of hyperextension and hyperflexion of the neck when managing the upper airway (laryngoscopy, intubation etc.) and positioning the patient
References :
- Lachhab IC, Dafiri R.
Une malformation à connaître : l’os odontoideum. A propos de deux cas pédiatriques.
Arch Pédiatr 2014 ; 21 : 388-91. - Kim HJ.
Cervical spine anomalies in children ans adolescents.
Curr Opin Pediatr 2013 ; 25 : 72-7.
Updated: February 2025