(cardiovocal syndrome)
Dysphonia due to paralysis of the left recurrent nerve as a result of mechanical compression or stretching caused by enlargement of cardiovascular or mediastinal structures in its path. This rare disease is due to compression of the left recurrent nerve as it makes its loop around the aorta, in the narrow space between the aortic arch, the ligamentum arteriosus (or ductus arteriosus) and the left pulmonary artery.
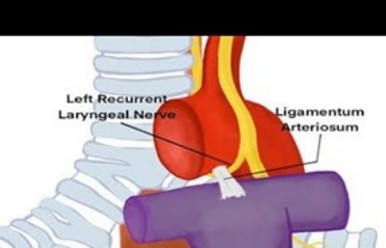
It can be observed :
- in adults: mitral stenosis, persistent patent ductus arteriosus, hypertension with dilatation of the left pulmonary artery, left heart decompensation, aortic arch aneurysm.
- in children: in cases of very wide ductus arteriosus, double outlet right ventricle, IVC or ICA with significant left-right shunt, Ebstein's anomaly or hypertension with dilatation of the left pulmonary artery.
Symptoms: dysphonia sometimes accompanied by stridor, poor swallowing.
Treatment: injection of hyaluronic acid or fat into the paralyzed cord.
Anesthetic implications:
recent cardiac work-up, gentle intubation, increased risk of post-intubation stridor
References :
- Hermans C, Manocha S, McLaughlin JE, Lipman M, Lee CA.
Ortner syndrome and haemophilia.
Haemophilia 2005; 11:548-51.
- Verbeke X, Vliebergh J, Sauer J, Leys M.
Hoarseness revealing Ortner’s syndrome.
Acta Clin Belg 2015; 70: 230.
- Murillo-Deluquez M, McKee C, Collazos-Noriega M, Clifford L. Cua CL, Tobias JD.
Ortner’s syndrome in an infant with congenital heart disease.
J Med Cases 2022;13(7):354-8
Updated: November 2024