Syndrome combining non-ossifying fibroids, giant cell granulomas in the jaw and café-au-lait spots. It is now considered a form of neurofibromatosis type I because it contains mutations of the NF1 gene (17q11.2). The main location of the fibroids is the tibia (78 %) with sometimes simultaneous involvement of the fibula. Sometimes associated with: mental retardation, hypogonadism (or early puberty), ocular abnormalities and cardiac malformation (mitral insufficiency, stenosis of the aortic isthmus), and, more rarely, kyphoscoliosis, chylothorax.
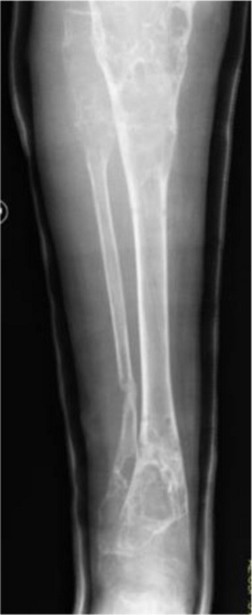
Anesthetic implications:
see Cherubism and von Recklinghausen syndrome
References :
- Stewart DR, Brems H, Gomes AG, Ruppert SL, Callens T et al .
Jaffe-Campanacci syndrome, revisited: detailed clinical and molecular analyses determine whether patients have neurofibromatosis type 1, coincidental manifestations, or a distinct disorder.
Genet Med 2014; 16: 448-59.
Updated: September 2021