[MIM 142 945, 142 946, 157 170, 236 100, 605 934, 609 408, 609 637, 610 828, 610 829, 612 530, 614 226]
(Arhinencephaly, median cleft syndrome, frontonasal dysplasia)
Prevalence: 1/10,000. Congenital brain malformation caused by an abnormality of the interhemispheric cleavage and the lack of olfactory stem. In general sporadic but rare familial cases exist (mutation in the SHH gene at locus 7q36).
It can be associated with:
- a chromosomal anomaly (37 %): trisomy 13 or 18, various deletions ; Pallister-Hall, Smith-Lemli-Opitz, Steinfeld syndromes (see those terms)
- a mutation of one of the following genes:
form HPE1: on 21q22
form HPE2: SIX3 gene (2p21)
form HPE3: SHH gene (7q36)
form HPE4: TGIF gene (18p11)
form HPE5: ZIC2 gene (13q22)
form HPE6: on 2q37
form HPE7: PTCH1 gene (9q22)
form HPE8: on 14q13
form HPE9: GLI2 gene (2q14)
form HPE10: on 1q41-q42
form HPE11: CDON gene (11q24)
form HPE12: CNOT1 gene (16q21)
form HPE13: STAG2 gene (Xq25)
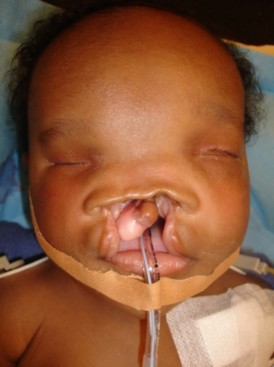
Clinical presentation: facial dysmorphism of varying degree (varying in severity from cyclopia to a median maxillary cleft with an unique incisive: hypotelorism, median facial cleft with cleft lip and palate, agenesis of the premaxilla with absence of the nasal ridge, see figure), mental retardation, frequent pituitary insufficiency (growth hormone, hypothyroidism and adrenal insufficiency, diabetes insipidus); absence or reduction of the interhemispheric fissure, total or partial indivision of the ventricles, fusion of the thalamus or the caudate nuclei.
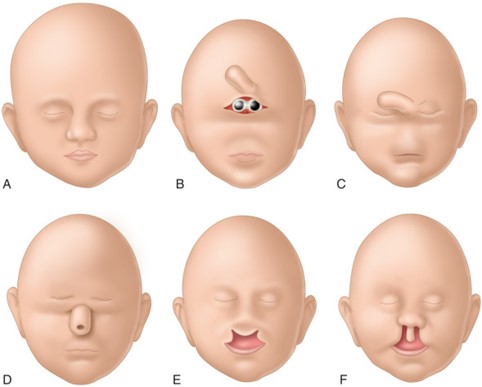
A: normal; B:cyclopia with 1 or 2 eyes in a single cavity, with or without proboscis
C: ethmocephaly with hypotelorism and proboscis; D:cebocephaly with hypotelorism and a single nostril
E: agenesis of the premaxilla (or medial cleft); F:bilateral cleft lip and palate
Three radiological forms are classicaly distinguished (De Myers classification) according to the degree of abnormality of the interhemispheric cleavage:
- alobar: merging of a single ventricle and the thalamus; absence of the corpus callosum, the falx, the olfactory bulbs and the optic tracts; sometimes hydrocephalus, microcephaly, cleft lip and palate, cardiac (VSD, dextrocardia) and genitourinary defects, panhypopituitarism; death before 1 year of age; aventriculy could be an extreme form of the alobar type
- semilobar: partially separated cerebral hemispheres; the ventricles are segmented and the thalamic fusion is partial; important mental retardation;
- lobar: the cerebral hemispheres are separated; mental retardation, visual, olfactory, and endocrine disorders, sometimes hydrocephalus; possible survival into adulthood.
- a 4th form, called syntelencephaly or interhemispheric variant, represents 2 to 15 % of the cases and is often associated with a mutation of the ZIC2 gene (13q32). There is a fusion of the frontal, posterior and parietal lobes, heterotopia of the grey matter, absence of the central part of the corpus callosum with a normal hypothalamus. There is a hypotelorism with discrete facial dysmorphism.
.jpg)
Sometimes isolated anosmia due to the lack of the olfactory stem. There is no clear correlation between the severity of the facial and brain abnormalities.
Anesthetic implications:
substitutive opotherapy (thyroid hormones and hydrocortisone); echocardiography; check blood electrolytes (risk of decompensation of diabetes insipidus); difficult face mask ventilation and intubation. Risk of hypo- and hyperthermia. Sometimes epilepsy.
References :
- Katende RS, Herlich A.
Anesthetic considerations in holoprosencephaly.
Anesth Analg 1987 ; 66 : 908-10. - Tung A, Anderson J, Daves S, Waggoner D, Kahana M.
Hypernatremia after cleft lip repair in a patient with holoprosencephaly (letter).
Anesth Analg 2006; 102: 965-6. - Dandena A, Sisay S, Mekonnen A, Beza K.
Aventriculy: a rare case report.
Reports in Medical Imaging 2021;14:9-13.
Updated: February 2021