(Oculo-auriculo-vertebral dysplasia, facio-auriculo-vertebral syndrome, hemifacial microsomia)
Prevalence between 1/3.500 and 5.600. Sporadic but a few cases of autosomal dominant transmission have been
reported. Boys are more often affected than girls (3:2) and the right side is most often involved than the left one. Malformative syndrome (unilateral microsomia) caused by abnormal development of the 2 first branchial arches with:
- unilateral mandibular hypoplasia with macrostomia; however the microsomia is bilateral and asymmetric in 20 to 30 % of the cases; sometimes facial paralysis or dysfunction of the auditory nerve ipsilateral to malformation
- microtia, pre-auricular appendages, middle ear malformations
- sometimes: maxillary hypoplasia, dental malocclusion and/or ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint
- congenital heart disease (20 %): ASD, VSD, conotroncal anomalies, ductus arteriosus
- deformity of the cervical (fusion or occipitalisation) or thoracic spine; sometimes spina bifida
- cleft palate (20 %)
- conjunctival desmoid tumors, sometimes microphthalmia or anophthalmia or eyelid coloboma.
- sometimes: hypoplasia of a lung, tracheobronchial anomalies (bronchus suis, pulmonary hypoplasia, esophageal atresia with or without fistula), agenesis of the ribs
- sometimes: limb anomalies: radius, thumb, feet
- sometimes: multicystic kidney, renal malformations, ureteral malformations
Intelligence is often normal but sometimes deep mental retardation; poor hearing associated.
Anesthetic implications:
echocardiography. XRays of the spine. Risk of difficult mask ventilation and intubation: mandibular hypoplasia, small mouth, neck stiffness; in case of intubation or nasogastric tube by the nasal route, make sure that there is no malformation of the base of the skull (risk of intracerebral penetration). The technique combining a classic laryngeal mask or Air - Q (wide breathing tube, absence of grids) and a fiberscopic intubation was used successfully. It is sometimes necessary to combine videolaryngoscopy and fiberoptic intubation.
Check the absence of vertebral malformations before making a neuraxial block.
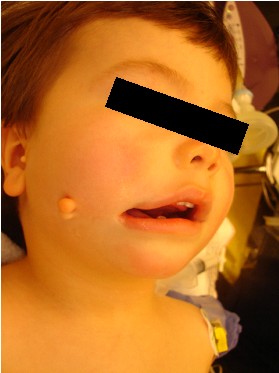
Macrostomia following hypoplastic right hemifacial and preauricular appendices
(pretragal fibrochondroma)
References :
- Johnson CM, Sims C.
Awake fibreoptic intubation via a laryngeal mask in an infant with Goldenhar's syndrome.
Anaesth Intensive Care 1994; 22:194-7. - Scholtes JL, Veyckemans F, Van Obbergh L, Verellen G, Gribomont BF.
Neonatal anaesthetic management of a patient with Goldenhar's syndrome with hydrocephalus.
Anaesth Intensive Care 1987; 15:338-40. - Madan R, Trikha A, Venkataraman R, Batra R, Kalia P.
Goldenhar’s syndrome : an analysis of anaesthetic management- a retrospective study of seventeen cases.
Anaesthesia 1990; 45: 49-52. - Allen F, Riopelle J, Sinha A.
Intracranial placement of a nasotracheal tube in a patient with Goldenhar syndrome associated with cribriform plate agenesis.
Anesth Analg 2011; 112: 198-200. - Suzuki E, Hirate H, Fujita Y, Sobue K.
Successful airaway management in a patient with Goldenhar syndrome using preoperative tridimensional computed tomography.
Anaesth & Intensive Care 2001; 39: 767-8. - Culnane T, Hullett B, Farrell T.
Pitfalls in pediatric tracheostomy: a case report.
Pediatr Anesth 2006; 16: 1281-4. - Char DS, Gipp M, Boltz MG, Williams GD.
Case report: airway and concurrent hemodynamic management in a neonate with oculo-auriculo-vertebral (Goldenhar) syndrome, severe cervical scoliosis, interrupted aortic arch, multiple ventricular septal defects and an unstable cervical spine.
Pediatr Anesth 2012; 22: 932-4. - Geneviève D, Captier G, Blanchet C.
Syndromes avec fentes labiopalatines.
In Syndromes dysmorphiques coordonné par Lacombe D et Philip N, Collection Progrès en Pédiatrie, Doin 2013, p 261-82. - www.orphananesthesia.eu
- Lokhande C, Riad I, Tetzlaff J, Ayad S.
The peri-operative management of a cesarean section in a patient with Goldenhar syndrome: a case report. J
Clin Anesth 2016; 34: 448-51. - Hasham F, van Helmond N, Sidlow R.
Anaesthesia and orphan disease: Difficult ventilation following intubation in Goldenhar syndrome.
Eur J Anaesthesiol 2017; 34: 181-3 - Sinha R, Pangasa N, Nethaji R, Maitra S.
Successful use of C-MAC Miller blade in a neonate with Goldenhar syndrome and cleft lip palate: a case report.
Acta Anaesth Belg 2019; 70: 39-41. - Partika ML.
Goldenhar syndrome with ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint: a case report.
A&A Practice 2021; 15 e01461 - Möhlenkamp E, Kohse EK, Sasu PB, Peters T, Grensemann J, Breitfeld P, Petzoldt M.
VivaSight single-lumen tube combined with hyperangulated videolaryngoscopy to rescue failed tracheal intubation in a patient with Goldenhar syndrome: a case report.
A&A Practice 2022;16:e01615.
Updated: October 2022