(Puretic syndrome, Murray-Puretic-Drescher syndrome, molluscum fibrosum, systemic hyalinosis)
Very rare. Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the CMG2 gene (capillary morphogenesis protein 2) on 4q21, coding for a transmembranar protein activated during capillary morphogenesis and which connects laminin to collagen IV via a von Willebrand A domain. Onset in infancy. Painful skin nodules with gingival hypertrophy, contractures in flexion of the joints, infiltration of neighboring tissues and maxillary osteolytic lesions. At histology: fusiform cells organized in bundles of collagen fibers.
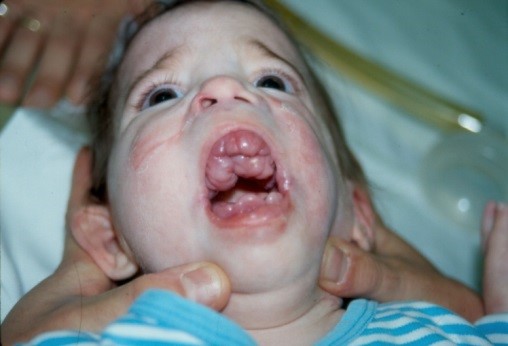
Anesthetic implications:
Difficult intubation: temporomandibular joint contracture, gingival hyperplasia, hyaline deposits in the trachea. Difficult positioning.
References :
- Vaughn GC, Kaplan RF, Tieche S, Downs JB.
Juvenile hyaline fibromatodsis : anesthetic management.
Anesthesiology 1990 ; 72 : 201-3.
- Norman B, Soni N, Madden N.
Anaesthesia and juvenile hyaline fibromatosis.
Br J Anaesth 1996 ; 76 : 163-6.
- Baraka AS.
Succinylcholine resistance in a patient with juvenile hyaline fibromatosis.
Anesthesiology 1997 ; 87 : 1250-2.
- Seefelder C, Ko JH, Padwa BL.
Fibreoptic intubation for massive gingival hyperplasia in juvenile hyaline fibromatosis.
Paediatr Anaesth 2000; 10: 682-4.
Updated: December 2019