Heterogeneous group of congenital muscle diseases that have common characteristics:
- a muscle weakness that is more or less progressive, often accompanied by amyotrophy and muscular contractures
- a histological picture showing muscle fibers of various sizes with areas of necrosis gradually replaced by fibrous or adipose tissue.
They were initially classified according to their topography, their evolution and age of the onset of the symptoms. The progress of molecular biology and genetics have greatly complicated this classification because we now know that a same phenotype can be caused by mutations in different genes and mutations of the same gene can produce different phenotypes.
These dystrophies are described in detail under their full name.
These are:
- progressive muscular dystrophy, or dystrophinopathies: Duchenne disease, Becker disease
- limb-girdle muscular dystrophy
- Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
- facio-scapulo-humeral muscular dystrophies
- congenital muscular dystrophies: Ullrich, Fukuyama, muscle-eye-brain etc.
- myotonic dystrophies
- oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
- distal muscular dystrophies
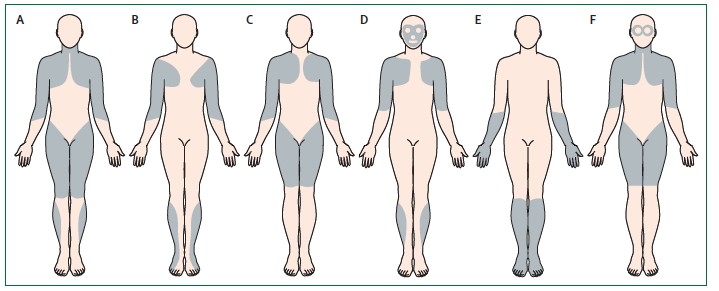
Topographic distribution of the muscle involvement in certain muscular dystrophies:
A: Duchenne, Becker; B: Emery-Dreifuss; C: myopathy of the girdles; D: facio-scapulo-humeral myopathy; E: distal muscular dystrophy; F: oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Anesthetic implications:
check the echocardiography, ECG and lung function; avoid succinylcholine because there is an increased risk of hyperkalemia; these pathologies are not myopathies linked to RYR-1 receptor (as the central core disease) and therefore the risk of malignant hyperthermia is not higher than that of the general population. The risk of anesthesia-induced rhabdomyolysis following exposure to halogenated agent is unknown.
References :
- Mercuri E, Muntoni F.
Muscular dystrophies.
Lancet 2013 ; 381 :845-60
Updated: July 2019