Unknown prevalence. Syndromic form of congenital lymphedema. Autosomal dominant transmittion with variable penetrance of a mutation of the FOXC2 gene (or MFH1 gene, on 16q24.3), coding for the transcription factor FOXC2 .
Clinical picture:
- primary lymphedema of the limbs, usually starting at puberty (but sometimes at birth or later), but occurring earlier in men
- associated with a distichiasis: this is a double row of supernumerary eyelashes at the level of the orifices of the Meibomian glands. It can be asymptomatic but may cause corneal irritation or ulceration
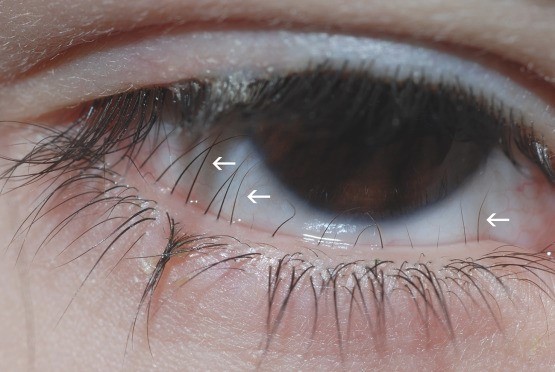
- sometimes: cardiac anomalies, cleft palate, varicose veins and extradural cysts.
- sometimes eye involvement: photophobia, ptosis, congenital ectropion and congenital cataract.
Anesthetic implications:
echocardiography, eye protection, avoid any trauma to the involved limb
References:
- Vignes S, Vidal F, Arrault M, Boccara O.
Les lymphoedèmes primaires de l’enfant.
Arch Pédiatr 2017; 24: 766-76
Updated: August 2017