(pelviscapular dysplasia)
Incidence < 1/106. Autosomal recessive transmission of a mutation of the TBX15 gene (1p12).
Association of:
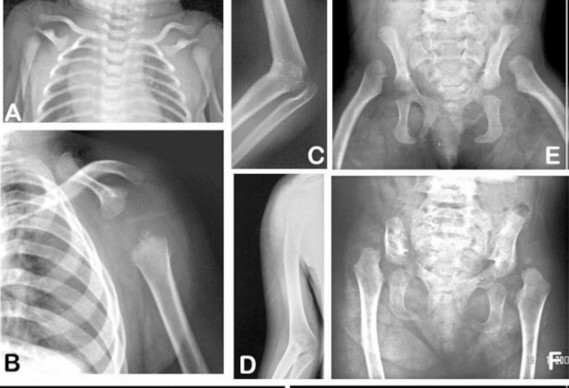
- pelviscapular dysplasia phenotypically similar to shoulder and pelvic dysplasia (Kosenow syndrome: see this term). X-Rays show aplasia of the blade of the scapula (A, B), hypoplasia of the iliac bone (E, F), humero-radial synostosis (C, D), dislocation of the femoral heads and moderate brachydactyly.
- epiphyseal abnormalities
- congenital dwarfism
- and facial dysmorphism characterized by frontal bossing, hypertelorism, narrow palpebral slits, sunken eyes, strabismus, malformed low-set posteriorly rotated, dysplasia of the aural pavilions, small chin, short neck with large skin folds and low implanted hair.
Intelligence may be normal or slightly diminished.
Anesthetic implications:
short stature, facial dysmorphism
References :
- Lausch E, Hermanns P, Farin HF,2 Alanay Y, Unger S, Nikkel S, Steinwender C, Scherer G, Spranger J, Zabel B, Kispert A, Superti-Furga A.
BX15 mutations cause craniofacial dysmorphism, hypoplasia of scapula and pelvis, and short stature in Cousin syndrome.
AM J Human Gen 2008 ; 83 :649-55
Updated: April 2022