Facial synkineses means the presence of involuntary movements of the face during a voluntary movement of another portion of the face. They are congenital or appear as a result of facial nerve paralysis. The most common varieties of facial synkineses are: mandibulo-palpebral-ptosis synkinesies or Marcus Gunn phenomenon (see this term), mandibulo-palpebro-frontal synkinesis, palpebro-auricular synkinesis and palpebro-platysmal synkinesis.
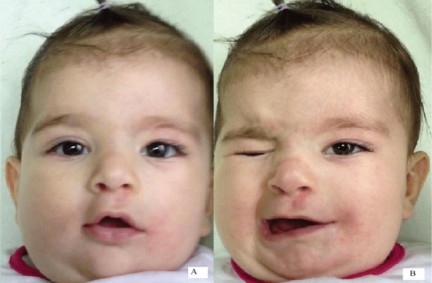
Mandibulo-palpebral synkinesis is an involuntary elevation of the upper eyelid when the lower jaw opens or moves to the opposite side. On the contrary, the Marin-Amat syndrome, or reverse Marcus Gunn phenomenon, consists in the closure of the eyelid when the patient opens its mouth or moves the mandible to the opposite side (see picture below). It is usually the result of facial paralysis but cases linked to a duplication of 12q have been described.
The mandibulo-palpebro-frontal, palpebro-auricular and palpebro-platysmal synkineses are variations of mandibulo-palpebral synkinesis. In case of mandibulo-palpebro-frontal synkinesis, the elevation of the contralateral eyebrows by the frontalis muscle triggers the involuntary closing of the opposite eyelid and of the lower jaw. Palpebro-platysmal synkinesis is an involuntary closure of the eyelids during voluntary contraction of the muscles of the neck. The palpebro-auricular synkinesis consists of involuntary movements of the ear during closure of the eyelids.
Acquired facial synkineses are observed following a facial paralysis and are probably due to an aberrant reinnervation.
Anesthetic implications:
A few cases of oculocardiac reflex during the handling of the ptotic eyelid have been described. Susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia has been suggested based on the histological examination of the involved muscles but has not been confirmed by any clinical cases (nor genetically).
References :
- Pandey M, Jain A, Sanwal MK, Vajifdar H.
Abnormal oculocardiac reflex in two patients with Marcus Gunn syndrome.
J Anaesth Clin Pharmacol 2011; 27: 398-9
- Myers KA, Innes AM, Mah JK-W.
Familial congenital facial synkinesis due to 12q duplication: a case report and literature review.
Pediatrics 2016; 138: e20161724
- Mansoor AM, Sullivan PD.
Images in Clinical Medicine. Intrafacial Synkinesis.
N Engl J Med. 2016; 374: 22 e27
Updated: December 2016