Very rare, belongs to the group of collagenous gastroenteropathies. Chronic gastritis with histological evidence of excess collagen (thick bands > 10µm) in the subepithelial zone and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lamina propria of the stomach. The origin is unknown. In children, symptoms include dyspepsia, abdominal pain and iron-deficiency anemia. In adults, complaints include chronic watery diarrhea, sometimes associated with colitis or celiac disease, with weight loss, abdominal distension and digestive bleeding. The adult form is often associated with an autoimmune pathology such as Sjögren's syndrome, lymphocytic gastritis or ulcerative colitis.
Endoscopy: appearance of mucosal nodules in the gastric body, due to mucosal atrophy in internodular areas. It is these atrophic areas that are pathological.
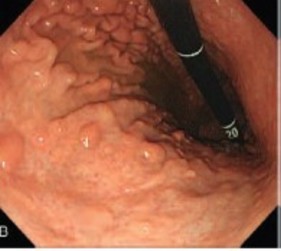
Treatment: long-term iron supplements, proton pump inhibitors (?), topical budesonide (capsules).
Anesthetic implications:
check hemoglobin level; IV iron treatment in case of anemia. Delayed gastric emptying ?
References :
- Kamimura K, Kobayashi M, Sato Y, Aoyagi Y, Terai S.
Collagenous gastritis: Review.
World J Gastrointest Endosc 2015 ; 7: 265-73
- Lee YJ, Lee M, Kim D-J, Lee S, HongJ.
Three case reports of collagenous gastritis in children : Lessons for an endoscopic and histologic approach to mucosal nodularity of the stomach.
Medicine 2019 ; 98 :11 e14870
Updated: July 2023