Prevalence: 1/15,000 to 1/30,000 births. Autosomal recessive transmission. Anomalies of the oxidation of long-chain fatty acids at the level of the mitochondria where carnitine palmitoyl-transferases ensure their transport across the mitochondrial membrane. It is one of the most frequent causes of myoglobinuria in young adults.
There are two forms:
- type I (CPT I): normal blood levels of carnitine, hepatosplenomegaly, sometimes renal tubulopathy
- type II (CPT II):
- either a multisystemic form: acute cardiac and hepatic failure in the neonatal period
- either a myopathic form: 3 clinical presentations 1) letal perinatal form 2) infantile form: muscle pains, contractures and myoglobinuria triggered by fasting, exercice and cold 3) adult form: muscular signs after strenuous exercice
- either episodes of hypoglycemia without ketosis
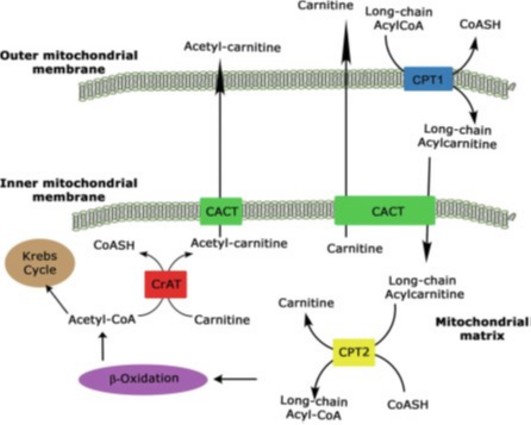
CPT1 : carnitine palmityl transferase type I
CPT2 : carnitine palmityl transferase type II
CrAT : carnitine acyltransferase
CACT : carnitine acylcarnitine translocase
Experimental treatment: bezafibrate (lipid-lowering agent)
Anesthetic implications:
avoid prolonged fasting, give glucose-containing IV fluids and measure blood glucose levels. Principles of a management of a mitochondrial cytopathy. Avoid continuous infusion of propofol. If total IV anaesthesia is required: dexmedetomidine, remifentanil, midazolam or remimazolam are preferable. In case of type II, the patients heterozygous for the mutation R503C could present a risk of metabolic reaction with rhabdomyolysis quite similar to dystrophinopathies (see Duchenne myopathy)
References :
- Neuvonen PT, van den Berg AA.
Postoperative coma in a child with palmitoyl-transferase I deficiency.
Anesth Analg 2001; 92: 646-7. - Hogan KJ, Vladutiu GD.
Malignant hyperthermia-like syndrome and carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency with heterozygous R503C mutation.
Anesth Analg 2009 ; 109 : 1070-2. - Benca J, Hogan K.
Malignant hyperthermia, coexisting disorders, and enzymopathies: risks and management options.
Anesth Analg 2009; 109: 1049-53. - Gentili A, Iannella E, Masciopinto F, Latrofa ME et al.
Rhabdomyolysis and respiratory failure : rare presentation of carnitine palmityl-transferase II deficiency.
Minerva Anestesiol 2008 ; 74 : 205-8. - Rocha CT.
Metabolic muscle disorders in infants and children.
J Pediatr Biochemistry 2014 ; 4 : 231-248. - Litman RS, Griggs SM, Dowling JJ, Riazi S.
Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility and related diseases.
Anesthesiology 2018; 129: 159-68.
Updated: February 2025