Acronym for Coloboma, congenital Heart disease, choanal Atresia, growth and development Retardation, Genital hypoplasia, Ears dysplasia.
Prevalence: classically 3.5/100,000 but seems more frequent (1/10,000 probably). In 60% of cases there is a mutation of gene CHD7 (8q12) coding for a helicase involved in the remodeling of chromatine. Most often sporadic (teratogenic agent ?).
The clinical criteria of clinical diagnosis are:
- major criteria: 1) ocular chorioretinal coloboma (80%), 2) uni- or bilateral choanal atresia or stenosis uni- or bilateral, and/or cleft palate; (3) internal ear semicircular canals hypoplasia (4) absence of the olfactory bulbs (arhinencephaly)
- minor criteria: 1) involvement of the cranial nerves, including the VIII (facial paralysis, eating disorders); (2) delayed puberty by lack of production of sex hormones (of pituitary origin): hypospadias, micropenis, cryptorchidism; (3) malformation of the external ear (pinna of special shape) or internal (hearing loss and equilibrium deficiency); ((4) cardiovascular anomalies (80%), tracheo-esophageal fistula ; 5) mental retardation.
There are thus:
- typical CHARGE syndrome: 3 major criteria, or 2 major + 2 minor
- partial CHARGE syndrome: 2 major criteria + 1 minor
- atypical CHARGE syndrome: 2 major criteria or 1 major + 2 minor.
In addition to the above definition criteria: micrognathia.
A kidney abnormality is present in 25 to 40% of the cases: unilateral agenesis, hypoplasia, urinary malformation.
Swallowing disorders and pulmonary aspiration are very common. Some cases of abnormal origin of the largevessels from the aortic arch (aberrant course of a carotid or a subclavian artery) have been reported.
CHARGE syndrome can be associated with a higher risk for pulmonary hypertension: cardiac malformations usually well tolerated evolve more rapidly to a severe PAH clinical picture.
Anesthetic implications:
difficult intubation (difficulty increases with age): the larynx and pharynx are narrower than normal, disorders of swallowing. Post-anesthesia respiratory problems especially if there is no cleft palate (operated or not) or in case of feeding difficulties justifying a gastrostomy or a fundoplication. Prophylaxis of endocarditis. Monitor renal function.
References :
- Stack CG, Wyse RK.
Incidence and management of airway problems in the CHARGE Association.
Anaesthesia 1991; 46:582-5. - Hoshi T, Matsumiya N, Satsumae T, Takahashi S, Sato K, Tanaka M.
A case of the CHARGE association with failed tracheal intubation (en japonais).
Masui 1998; 47:487-9. - White DR, Giambra BK, Hopkin RJ, Daines CL, Rutter MJ.
Aspiration in children with CHARGE syndrome.
Intern J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2005; 1205-9. - Blake K, MacCuspie J, Hartshorne TS, Roy M, Davenport SLH, Corsten G. Postoperative airway events of individuals with CHARGE syndrome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2008;72: 1311-1316
- Wilson MA, Grimmer JF, Hawkins J.
Carotid anomaly in CHARGE association: a case report.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol Extra 2011; 6: 85-6. - Shimizu S, Koyama T, Mizota T, Fukuda K.
Successful intubation with the Glidescope in patient with CHARGE syndrome.
J Anesth 2013; 27: 965-6. - Salomon R.
Syndromes avec anomalies rénales in
Progrès en Pédiatrie : syndromes dysmorphiques par Lacombe D et Philip N, Doin 2013, p 139-50
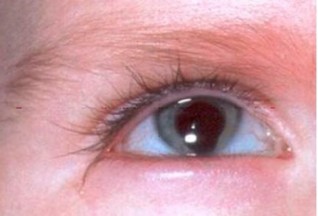
iridic coloboma
Updated: August 2017