Group of malformations of the neuraxis including the brainstem, the cerebellum, the 4th ventricle and the cervical spine.
Different types:
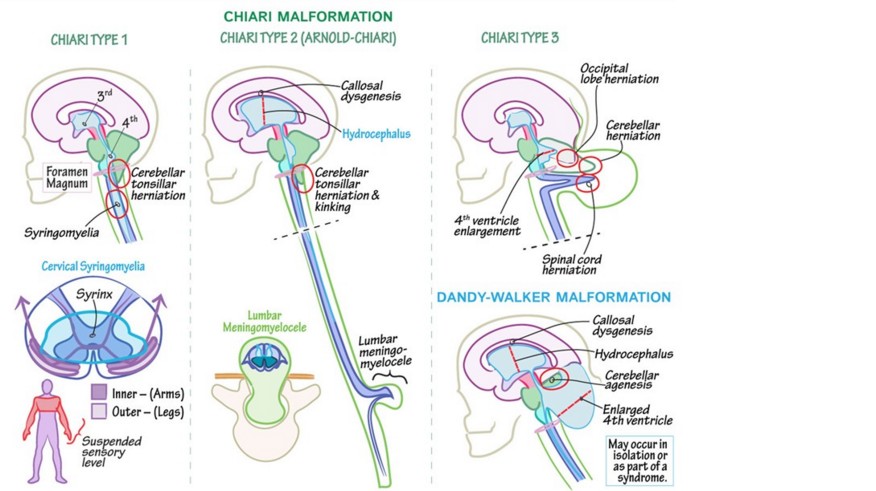
- type I: coning of the cerebellar tonsils (more than 5 mm below the foramen magnum at MRI).
This anomaly can be associated with:
- cervical spinal dysmorphism: stretching, kinking, hydromyelia, hydrocephalus
- syndromic craniosynostosis, including Crouzon (70%) or Pfeiffer (50%) syndromes due to the hypoplasia of the posterior part of the skull, causing also a compression of the respiratory centers and an obstruction to cerebral venous return; in these cases, occipital decompression may correct the associated central sleep apnea syndrome.
- intracranial hypotension due to leakage of CSF: in these cases, repair of the leak corrects the x-ray picture and the symptoms of intracranial hypotension.
- type II: generally associated with a meningomyelocele; displacement of the vermis, the 4th ventricle, the bulb and the lower part of the pons into the cervical canal
- type III: associated with an occipital encephalocele
- type IV: severe (rare) cerebellar hypoplasia associated with a meningomyelocele
Anesthetic implications:
swallowing problems and risk of inhalation of pharyngeal or gastric contents. Risk of paralysis of the vocal cords (stridor). Breathing disorders during sleep: obstructive and/or central (often undiagnosed) apnea. Risk of intracranial hypertension (most often, a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is present ). In case of meningomyelocele: risk of latex allergy.
In case of type I, flexion of the neck moves the cerebellum tonsil downwards (1,4 mm on average). It can block the flow of CSF and cause acute intracranial hypertension and compression of nerve structures. Extension of the neck has a reverse effect, which may explain the spontaneous position in opisthotonos in some patients. That must be taken into account for laryngoscopy and positioning of the head during a procedure. Non-invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure (measurement of the external diameter of the optic nerve by ultrasound) and cerebral blood flow (transcranial Doppler).
References :
- Ruff ME, Oakes WJ, Fisher SR, Spock A.
Sleep apnea and vocal cord paralysis secondary to type I Chiari malformation.
Pediatrics 1987; 80:231-4. - Radhakrishna S.
Coning in a patient with spina bifida following general anaesthesia for cystoscopy.
Anaesthesia 2000; 55:295-6.
- Cakmakkaya OS, Kaya G, Altintas F, Bakan M, Yildirim A.
Anesthetic management of a child with Arnold-Chiari malformation and Klippel-Feil syndrome.
Pediatr Anesth 2006; 16:355-6. - Adler F, Gupta N, Hess CP, Dowd CF, Dillon WP.
Intraosseous CSF fistula in a patient with Gorham disease resulting in intracranial hypotension.
AJNR 2011; 32, E198-E200. - Addo NK, Javadpour S, Kandasamy J, Sillifant P, May P, Sinha A.
Central sleep apnea and associated Chiari malformation in children with syndromic craniosynostosis: treatment and outcome data from a supraregional craniofacial center.
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 2013; 296-301. - Tubbs RS, Kirkpatrick CM, Risk E, Chern JJ, Oskouian RJ, Oakes WJ.
Do the cerebellar tonsils move during flexion and extension of the neck in patients with Chiari type I malformation ? A radiological study with clinical implications.
Childs Nerv Syst 2016 ; 32 : 527-30. - Soued M, Le Gouez A, Mercier FJ.
Anesthetic management of a patient with Arnold Chiari malformation and syringomyelia during laparoscopic surgery with neurologic monitoring: a case report.
A&A Practice 2025;19:e01908
Updated: February 2025